Skin Pigmentation Compounding Pharmacy in Australia
At Zenith Pharmacy, we specialise in creating personalised treatments designed to target skin pigmentation concerns. Our compounded formulations are tailored to suit different skin types, sensitivities and clinical needs. Whether you’re managing melasma, dark spots or post acne pigmentation, we prepare customised solutions to support clearer, more even toned skin.
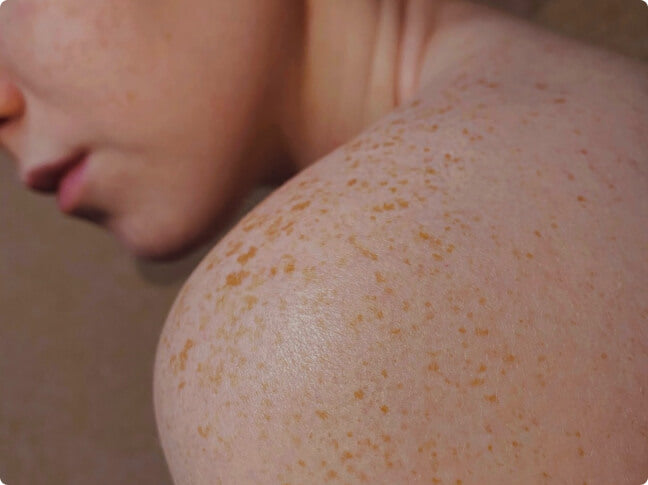

Dark Spots on the Skin: A Common Pigmentation Concern
Skin pigmentation concerns are extremely common, and many people experience dark spots on the face or body at some point in their lives. These changes can be worrying or frustrating, whether they stem from a diagnosed pigmentation condition, ageing, sun exposure or post-acne marks. As a compounding pharmacy for pigmentation, we understand how important personalised treatment can be.
Pigmentation disorders occur when melanocyte cells, the cells responsible for producing melanin, the pigment that gives skin its colour, become damaged or start functioning differently. This usually affects small, specific areas of the skin. When too much melanin is produced, it leads to hyperpigmentation, creating darker patches. When too little is produced, hypopigmentation can appear as lighter spots on the skin.
Common prescription and over-the-counter options for managing these concerns include hydroquinone cream, kojic acid preparations, tretinoin, azelaic acid and Vitamin C serums. Compounded pigmentation treatments allow these ingredients to be customised to your skin type, sensitivity and specific pigmentation needs, offering a more targeted approach.

Understanding the Causes of Skin Pigmentation
Pigmentation conditions occur when the skin produces too much or too little melanin. Common forms of hyperpigmentation include age spots (lentigines), dry and dark velvety patches known as acanthosis nigricans, and raised age-related spots called seborrhoeic keratoses. These conditions are generally harmless but can make the skin look uneven or dull.
Individuals with African, Asian, Indian or Polynesian skin types often experience dermatosis papulosa nigra, a benign condition that appears as multiple small, raised dark spots on the face and neck.
Pigmentation changes can also occur after inflammation or injury. This includes post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (dark marks) and post-inflammatory hypopigmentation (light patches), commonly seen after acne, dermatitis, eczema, or any trauma to the skin. These conditions develop when healing triggers irregular melanin production, leaving behind uneven skin tone.
Other genetic conditions that can impact melanin production in the skin cells
-
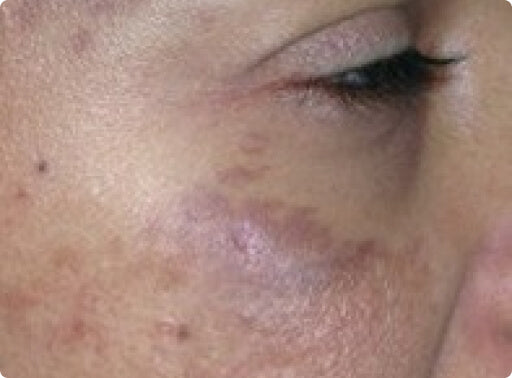
Naevus of Ota
Naevus of ota are darker birthmark smooth spots and patches that are coloured brown grey or blue. People are generally born with the pigmentation. The naevus of ota refers to a patch on the side of the forehead or around the eye.
-
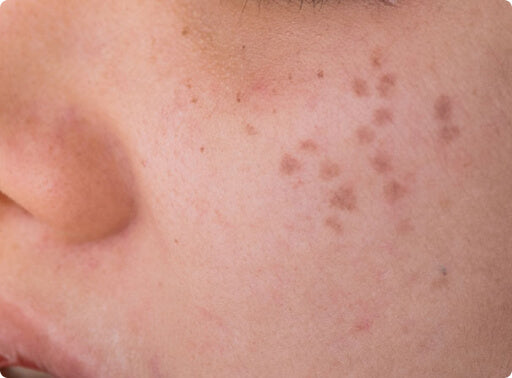
Hori’s Naevus
Hori’s naevus is a benign pigmentation condition that appears as blue grey or brownish patches on the cheeks. It typically develops in adulthood and is most commonly seen in women of Asian heritage. This condition occurs when melanin producing cells gather deeper in the skin, leading to stubborn facial discolouration that often requires targeted treatment.
-

Albinism
Albinism is a rare, inherited genetic condition where the body produces little to no melanin, the pigment responsible for colouring the skin, hair, and eyes. Because melanin also plays an important role in eye and visual development, people with albinism may experience lighter skin and hair along with vision related challenges. The condition is present from birth and requires long term skin and eye care.
-
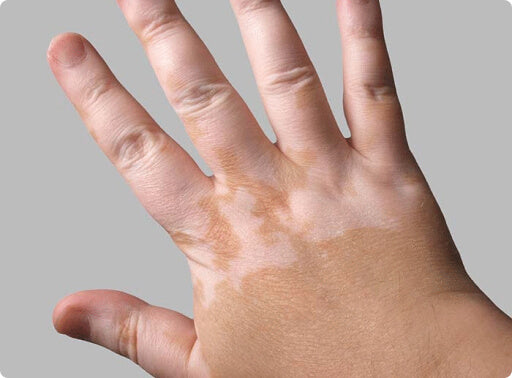
Vitiligo
Vitiligo is a common condition where lighter patches appear on the skin. The white spots and patches are caused when the cells that produce the skin-colouring hormone melanin are damaged or destroyed. It can be a small patch or across significant areas of your skin. About one in 10 people who experience vitiligo have a family history of the condition.
-

Melasma
Melasma is a common skin condition where dark spots develop on the face, neck and body. It is common in areas that are more exposed to the sun, such as the forehead and cheeks. Similar to lentigines (freckles), these are dark areas where more melanin was produced.
Treatments for Pigmentation
-
Hydroquinone
Hydroquinone is a formulation that can reduce pigmentation in the skin. It is known as a skin-bleaching agent, a hyperpigmentation treatment, a pigmentation removal cream or a pigmentation cream.
It is used as a topical hydroquinone cream, which can be formulated as a hydroquinone compound cream. It is used for treating areas of hyperpigmentation, such as melasma. Hydroquinone creams in Australia include over the counter products and more concentrated pharmacy-only products.
-
Tretinoin
Tretinoin or retinoic acid is a Vitamin A formula and an antioxidant medication. Tretinoin cream can partially reverse the impact of sun exposure, reducing the appearance of fine lines and lightening pigmentation on the skin.
It is a topical formulation that comes as a pharmacy product – Tretinoin 0.05 cream – in Australia.To purchase Tretinoin in Australia you will require a valid prescription from a doctor.
-
Kojic acid
Kojic acid is another medication that bleaches the skin by stopping the production of melanin. It is also used in as a kojic acid cream or kojic acid serum for hyperpigmentation treatment. For post inflammatory hyperpigmentation treatment or for melasma, this is one of the creams to remove dark spots on skin. In Australia, kojic acid is available over the counter and with a prescription.
-
Vitamin C Serum
Vitamin C serums (ascorbic acid) also act as skin-lightening products to aid hyperpigmentation. It is a type of antioxidant that stimulates the collagen cells in the skin to repair. It can improve fine lines and reduce inflammation.
Vitamin C must be in the right formulation to be effective as it is unstable when exposed to air, light or heat.









